Series 160, wound Primary
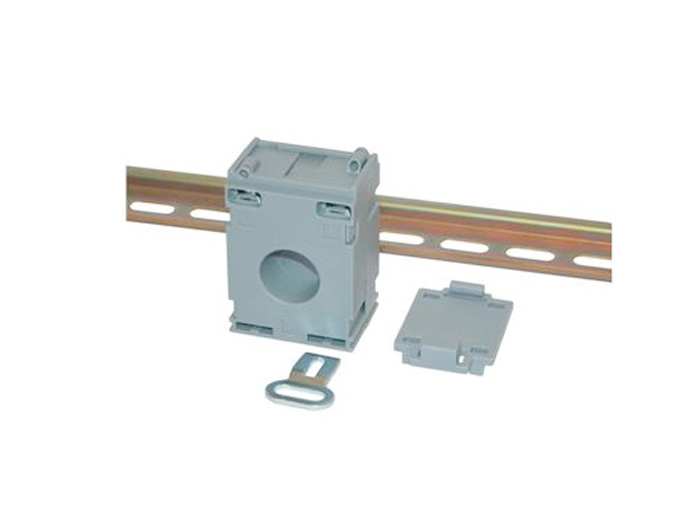

Series 13, 21mm Dia Cables
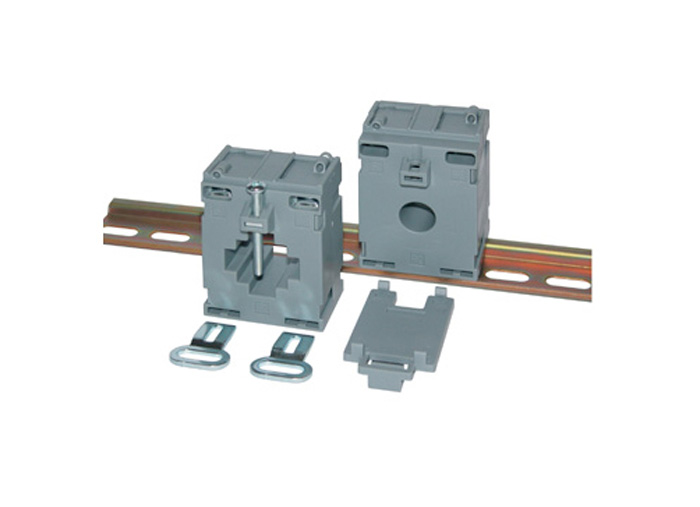

Series 14, 20/30mm Busbars

Series 162, 20mm Busbars

Series 163, 20/30mm busbars
Series 164, 30/40mm Busbars

Series 173, 20/30mm Busbars

Series 174, 30/40mm Busbars

Series 175, 40/50mm Busbars

Series 18, 50/60mm Busbars

Series 19, 60mm Busbars

Series 20, 60/80mm Busbars

Series 21, 80/100mm Busbars

Series CTH101L, 100x50mm Busbars

Series 127, 127×38 or 127×54 Bars

Three Phase Current Transformers

Moulded Case Rectangular Current Transformers

UL Recognised Range (ANSI/IEEE spec)
What are Moulded Case Current Transformers Used For?
Moulded Case Current Transformers (MCCT) are types of instrument transformer used in electrical power systems for current measurement and protection purposes. It is primarily designed to step down high electrical currents to a standardised and measurable value that can be easily used by protective relays, meters, or other monitoring devices.
MCCTs are commonly used in circuit breaker applications, where they provide current measurements for various protective functions, such as overcurrent protection, differential protection, and earth fault protection. They are also used in power quality monitoring, load monitoring, and energy management systems.
The construction of an MCCT typically involves a secondary winding wound around a magnetic core. The primary conductor, carrying the current to be measured, is passed through the opening or window in the MCCT. The ratio of the primary current to the secondary current is determined by the number of turns in the windings and the core characteristics. The secondary winding output is then connected to the measuring or protection devices.
The main advantages of using MCCTs include electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits, accurate current measurement, and the ability to step down high currents to a safe and manageable level for measurement. Additionally, MCCTs are designed to withstand high fault currents and provide reliable and accurate performance under various operating conditions.
Overall, MCCTs play a crucial role in electrical power systems by providing current measurements for monitoring devices, enabling efficient and safe operation of the power network.
Any Questions
For further information on any of our products please fill in our call back request form, and one of our dedicate sales team will call you.
Alternativley you can call us direct on:
+44 (0)1922 640003